This PedsCases Note provides a one-page infographic on Drug-Induced Epidermal Necrolysis (DEN). DEN is a delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction to drugs or their metabolites resulting in a severe mucocutaneous blistering eruption. It was created by Kylie Peake (Medical Student, University of British Columbia) & Dr. Joseph Lam (Pediatric Dermatologist, University of British Columbia)
Click the Image below for a full page PDF
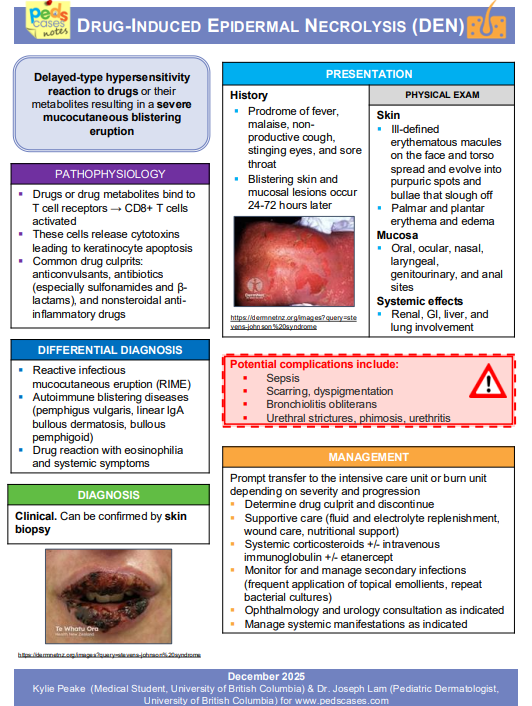
Related Content:
References:
- Ahluwalia J, Wan J, Lee DH, Treat J, Yan AC. Mycoplasma-associated Stevens-Johnson syndrome in children: retrospective review of patients managed with or without intravenous immunoglobulin, systemic corticosteroids, or a combination of therapies. Pediatr Dermatol. 2014;31(6):664-669. doi:10.1111/pde.12481
- Gavigan GM, Kanigsberg ND, Ramien ML. Pediatric Stevens-Johnson Syndrome/Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis Halted by Etanercept. J Cutan Med Surg. 2018;22(5):514-515. doi:10.1177/1203475418758989
- Hasegawa A, Abe R. Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis: Updates in pathophysiology and management. Chin Med J (Engl). 2024;137(19):2294-2307. doi:10.1097/CM9.0000000000003250
- Jeong MS, Choi YY, Ahn YH, Lee K, Park JS, Suh DI. Etanercept treatment for pediatric toxic epidermal necrolysis induced by deflazacort: a case report and literature review. Front Immunol. 2024;15:1342898. Published 2024 Jan 25. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2024.1342898
- McPherson T, Exton LS, Biswas S, et al. British Association of Dermatologists' guidelines for the management of Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis in children and young people, 2018. Br J Dermatol. 2019;181(1):37-54. doi:10.1111/bjd.17841
- Noe MH, Micheletti RG. Diagnosis and management of Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis. Clin Dermatol. 2020;38(6):607-612. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2020.06.016
- Ramien M, Goldman JL. Pediatric SJS-TEN: Where are we now?. F1000Res. 2020;9:F1000 Faculty Rev-982. Published 2020 Aug 13. doi:10.12688/f1000research.20419.1
- Ramien ML, Mansour D, Shear NH. Management of Drug-Induced Epidermal Necrolysis (DEN) in Pediatric Patients: Moving from Drug-Induced Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, Overlap and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis to a Single Unifying Diagnosis of DEN. Paediatr Drugs. 2022;24(4):307-319. doi:10.1007/s40272-022-00515-0
- Ye LP, Zhang C, Zhu QX. The Effect of Intravenous Immunoglobulin Combined with Corticosteroid on the Progression of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome and Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis: A Meta-Analysis. PLoS One. 2016;11(11):e0167120. Published 2016 Nov 30. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0167120
- Images:
- DermNet. 2018. SJS-TEN Oral. https://dermnetnz.org/topics/sjs-ten-images
- Te Whatu Ora. Health New Zealand. 2018. SJS-TEN Images. https://dermnetnz.org/images?query=stevens-johnson%20syndrome
An author of this Note has financial support from La Roche Posay Canada, Pfizer
File:
Physiologic System:
Clinical Presentation:
